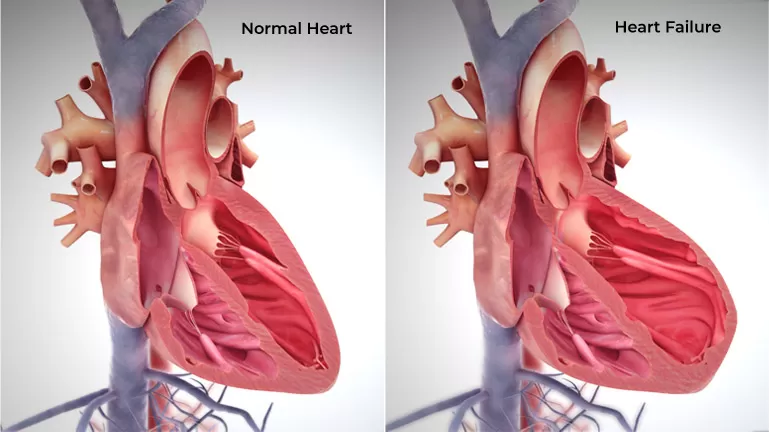
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive condition in which the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs for blood and oxygen. Basically, the heart can’t keep up with its workload. In acute heart failure, the symptoms appear suddenly but go away fairly quickly. This condition often occurs after a heart attack. It may also be a result of a problem with the heart valves that control the flow of blood in the heart.
In chronic heart failure, however, symptoms are continuous and don’t improve over time. The vast majority of heart failure cases are chronic
The symptoms of heart failure may include:
To diagnose heart failure, your doctor will ask you questions about your medical history, talk about your symptom(s) and do a physical examination. This will include checking your heart rate and rhythm, taking your blood pressure, and checking if you have fluid in your lungs, legs and other parts of your body. In most cases you will also have further tests to confirm the diagnosis and guide how your symptoms are controlled.
You may hear your doctor talk about the ‘ejection fraction’ of your heart. This refers to the amount of blood that is pushed out of your left ventricle every time your heart beats. It’s usually expressed as a percentage – over 50% is considered normal.
Some people with heart failure have a normal ejection fraction, so ejection fraction is used alongside other tests to help diagnose heart failure.
A single risk factor may be enough to cause heart failure, but a combination of factors also increases your risk.
Risk factors include:
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
Common treatments include:
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.